TLDR
When it comes to tanning, UV index plays a vital role in determining the strength and intensity of ultraviolet rays that reach your skin. The UV index is a scale that measures the UV rays at any time of the year, depending on the position of the sun. It ranges from 0 to 10, with higher values indicating a greater risk of damage to your skin.
Protecting Your Skin from UV Damage
On a typical day in the Southern Hemisphere, where the sun’s position brings more ultraviolet radiation, it’s crucial to understand how to protect your skin, especially if you plan to spend time outdoors between 10 AM and 4 PM. At these hours, when the UV index is higher, the risk of skin damage is increased, so applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen and wearing protective gear like a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses, and long-sleeved tops is essential. You can quickly check the UV index using Google or your smartphone’s weather app to determine whether the conditions are safe for tanning.

Tanning occurs because UV radiation triggers the release of melanin, a pigment in your skin. UVA radiation activates the melanin already in your skin, while UVB radiation stimulates your body to produce more melanin, resulting in a sun tan. However, tanning too long in high UV index conditions can lead to burning and sun damage, even if it appears to give you that desirable glow. It’s important to aim for moderate UV conditions to get the best UV index for tanning, which falls between 3 and 5, ensuring a balance between achieving a healthy tan and protecting yourself from skin cancer and premature aging.
Dermatologist Explained About UV Index
Reasons to Understand UV Index for Your Skin Tone.
Remember, your location, altitude, and proximity to reflective surfaces like water or snow can also influence the intensity of UV rays. So, whenever you’re out, especially during the summer months, staying in the shade or limiting exposure. Using a tan accelerating body lotion like Base Tan can help speed up the tanning process, even in low UV conditions. If you plan to be outdoors for an extended time, using Smart Screen, a broad-spectrum SPF 20, is the best option for protecting your skin while allowing for safe tanning and maintaining skin health.
Understand UV Index & Level Of Harmful UV Rays For Your Skin Tone
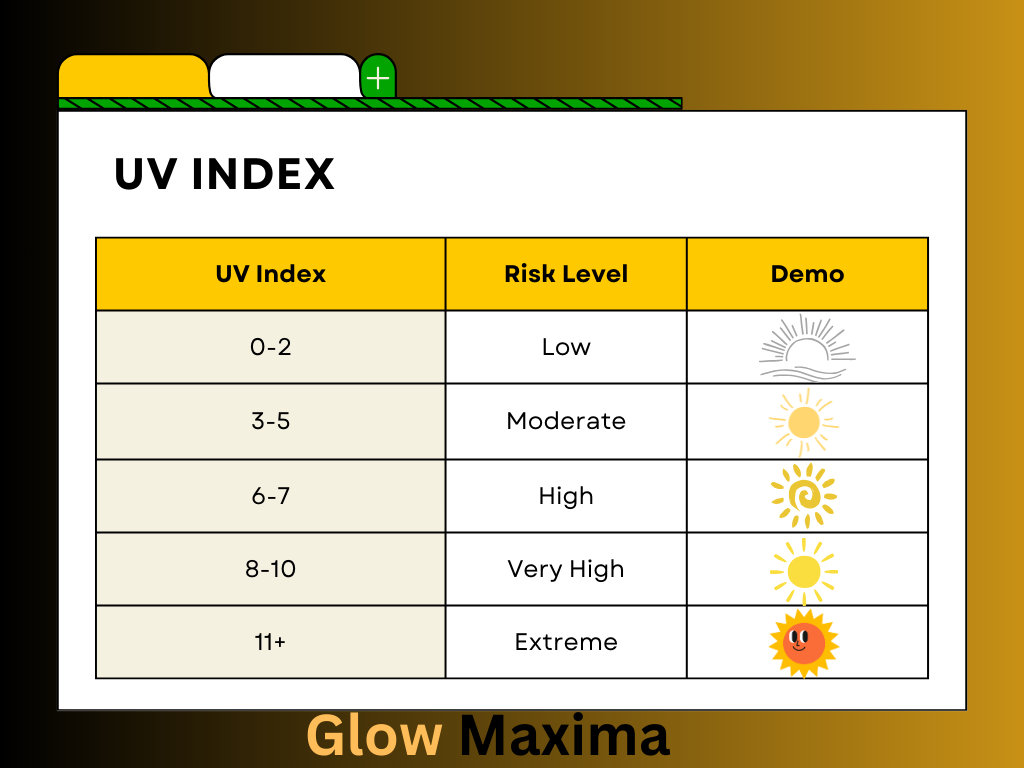
When it comes to tanning, understanding the UV Index is essential for protecting your skin while still getting that sun-kissed glow. The UV Index ranges from 0 to 11+, and each level requires different strategies to ensure safe tanning. Let’s break it down by numbers and explore the best way to tan safely at different UV levels.
UV Index 0 to 2: Low Risk
If the UV Index is between 0 and 2, you’re in the ideal range for gentle tanning. These are perfect conditions for outdoor activities like taking a walk or enjoying the sun before 10 a.m. or after 4 p.m.. It’s still important to wear sunscreen with SPF 30+ for fair skin and SPF 15+ for medium and dark skin tones. During this low-risk time, those with light skin should limit sun exposure to 30-60 minutes, while medium and dark skin tones can safely tan for 1-2 hours or slightly longer thanks to their natural UV resistance.
UV Index 3 to 5: Moderate Risk

As the UV Index rises to between 3 and 5, the risk is moderate, meaning safe tanning is still possible with the right protection. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen SPF 30+ and wear protective clothing during the less intense sun hours. If you have light skin, you’ll need a high SPF and should keep tanning sessions to no more than 30 minutes. For medium skin, SPF 30+ is sufficient, allowing you to tan safely for about 1 hour. Those with dark skin can also enjoy extended tanning time but should still use SPF 15+ for full protection.
UV Index 6 to 7: High Risk
A UV Index between 6 and 7 presents a high risk for skin damage, so extra caution is necessary. At this level, SPF 50 is strongly recommended, and it’s best to limit tanning to the early morning or late afternoon. For those with light skin, it’s important to avoid tanning for more than 15-20 minutes even with SPF 50+. Medium skin tones can manage under 45 minutes with SPF 30+, while dark skin tones can tan for about 1 hour but should still be cautious.
UV Index 8 to 10: Very High Risk

When the UV Index reaches 8 to 10, the risk of UV exposure is very high. It’s crucial to use maximum protection like SPF 50+ and avoid tanning during peak hours. For light skin, tanning should be avoided completely or limited to 15 minutes with SPF 50+. Medium skin types need high SPF and should tan for no longer than 30 minutes, while dark skin can handle limited tanning time but must use SPF 30+ to avoid potential damage.
UV Index 11+: Extreme Risk
At a UV Index of 11+, the risk is extreme, and it’s best to avoid sun exposure altogether. If you absolutely need to be outside, stay in the shade and use high-factor sunscreen every two hours. Light skin should prioritize staying indoors, while medium skin needs very high SPF and should limit any outdoor activities. Dark skin still requires SPF 30+ to avoid UV damage, and all skin tones should follow safe tanning practices to minimize UV radiation risks.
UV Index Tanning Guide: Skin Protection Tips
Understanding the UV Index is important for getting a safe tan based on your skin type. The sun’s strength increases with a higher number, which means a greater risk of skin damage, aging, and even skin cancer. To enjoy the sun between a UV Index of 3 to 5, use broad-spectrum natural sunscreen with Zinc Oxide to protect against UVA and UVB rays. With the right SPF rating, such as SPF 30 that blocks 97% of UVB rays, you can experience gradual tanning and a reduced risk of harm.
Make sure your sunscreen blocks UV rays properly, as the right SPF can reduce the risk of sun damage while allowing you to absorb some sunlight for Vitamin D, which is essential for your bones and immune health. It’s all about finding a balance—too much sun can damage skin, while too little can lead to Vitamin D deficiency. Always check the UV Index daily, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours to tan safely and keep your skin healthy.
Alternatives to Excessive Tanning for Reducing Skin Cancer Risk
Prolonged exposure to UV rays can lead to severe skin damage, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Fortunately, there are healthier options for achieving that desired tan without risking your skin well-being. Using self-tanners, such as lotions, creams, which react with the top layer of the skin to darken its appearance, is a safe way to get a natural-looking tan. If you prefer a quicker option, spray tans offer an instant tan, with a fine mist of tanning solution evenly sprayed over your body at professional salons. These alternatives carry no risk of UV damage and can give you a sun-kissed glow or a deep bronze, depending on your preference.
Key Tips for Tanning Without Sunburn
- Achieving a healthy tan without getting sunburn requires careful preparation and protection.
- It’s important to understand the UV index, which measures the strength of ultraviolet rays from the sun.
- The sun is strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so minimize exposure during these hours and consider tanning in the early morning or late afternoon to reduce the risk of overexposure to harmful rays.
- Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining skin health and aiding melanin production, which gives color and helps protect your skin from damage.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF 30 or higher as the first line of defense against harmful UV radiation.
- Apply a sufficient amount for full body coverage and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying, since sunscreen’s effectiveness diminishes over time.
- A good moisturizer can keep moisture in, adding an extra layer of protection against dryness and peeling.
Wrapping Up and My Experience With Safe Tanning
My journey into skin health began after years of working in the harsh Australian sun, which led to a skin cancer scare. That was my wake-up call to rethink my approach to sun exposure and the chemical exposure from many Sun care products on the market. Now, I always prioritize using natural, organic sunscreen to protect my skin from excessive UV exposure. As an outdoor enthusiast, I’ve learned to respect my skin’s limits while enjoying the sun. It’s essential to play it smart by using sunscreen daily, especially when working or playing outside most days.
FAQ
Can you tan with a UV index of 1?
With the lowest UV index between 1 and 2, there is low exposure to UV light. According to the US Environmental Protection Agency, there’s no protection needed at this level, and you can safely stay outside with minimal sun protection. However, it’s contradictory since you can still get a sunburn, though it’s unlikely. Tanning at UV 1 or 2 is possible but will probably take a while.
What UV index is best for tanning?
A UV index between 3 and 5 is generally safer for tanning. However, it’s important to protect your skin with sunscreen. Higher UV indexes can increase the risk of skin damage.
Can you get tan with a UV index of 4?
Yes, you can still tan with a UV index of 4, but it’s considered moderate. Tanning may happen slower, so using sunscreen to protect your skin is essential.
How long does it take to get a tan in UV 7?
Tanning with a UV index of 7 is not safe. Sun exposure at this level increases the risk of skin cancer, and despite the uplifting feeling from the sun, the risks may outweigh the benefits.
Why do we tan?
Exposure to UV radiation triggers the release of melanin in the skin. UVA radiation darkens existing pigment cells, while UVB radiation stimulates the body to produce more melanin, causing a sun tan. However, too much sun exposure can cause burning and sun damage. It’s best to tan with the UV index at moderate levels and follow guidelines to prevent skin cancer.
When is UV radiation at its highest?
UV radiation is highest between 10 AM and 3 PM on a cloudless summer day. During this time, wearing sunscreen and protecting sensitive areas like the eyes, lips, and scalp is essential. Applying SPF 30 sunscreen every 2 hours ensures continuous protection from sunburn and UV damage.
Can you still tan with sunscreen?
Yes, you can still tan with sunscreen. Although sunscreen filters harmful UV rays, it doesn’t block all UV, so tanning can still occur while reducing the risk of sunburn.
Should I wear sunscreen in a tanning bed?
Yes, it’s important to wear sunscreen in a tanning bed to protect your skin from UV radiation. However, it’s best to avoid tanning beds entirely due to the high risk of skin damage.
How high does the UV index have to be to tan?
You can tan when the UV index is around 3. Make sure to use protection, as even low UV index levels can cause skin damage over time.
Can you tan in the shade?
Yes, you can tan in the shade because of indirect sunlight and reflected UV rays, but the process will be slower. Wearing sunscreen is still important.
What is the best UV index for tanning?
A sun tan requires exposure to ultraviolet UV radiation. The best time to tan without burning is to use protection against the harmful effects of UV rays and always see index 0-2 Low to 3-5 Moderate risk level in your area. These are the best ways to tan safely.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column] [/et_pb_row] [/et_pb_section]
